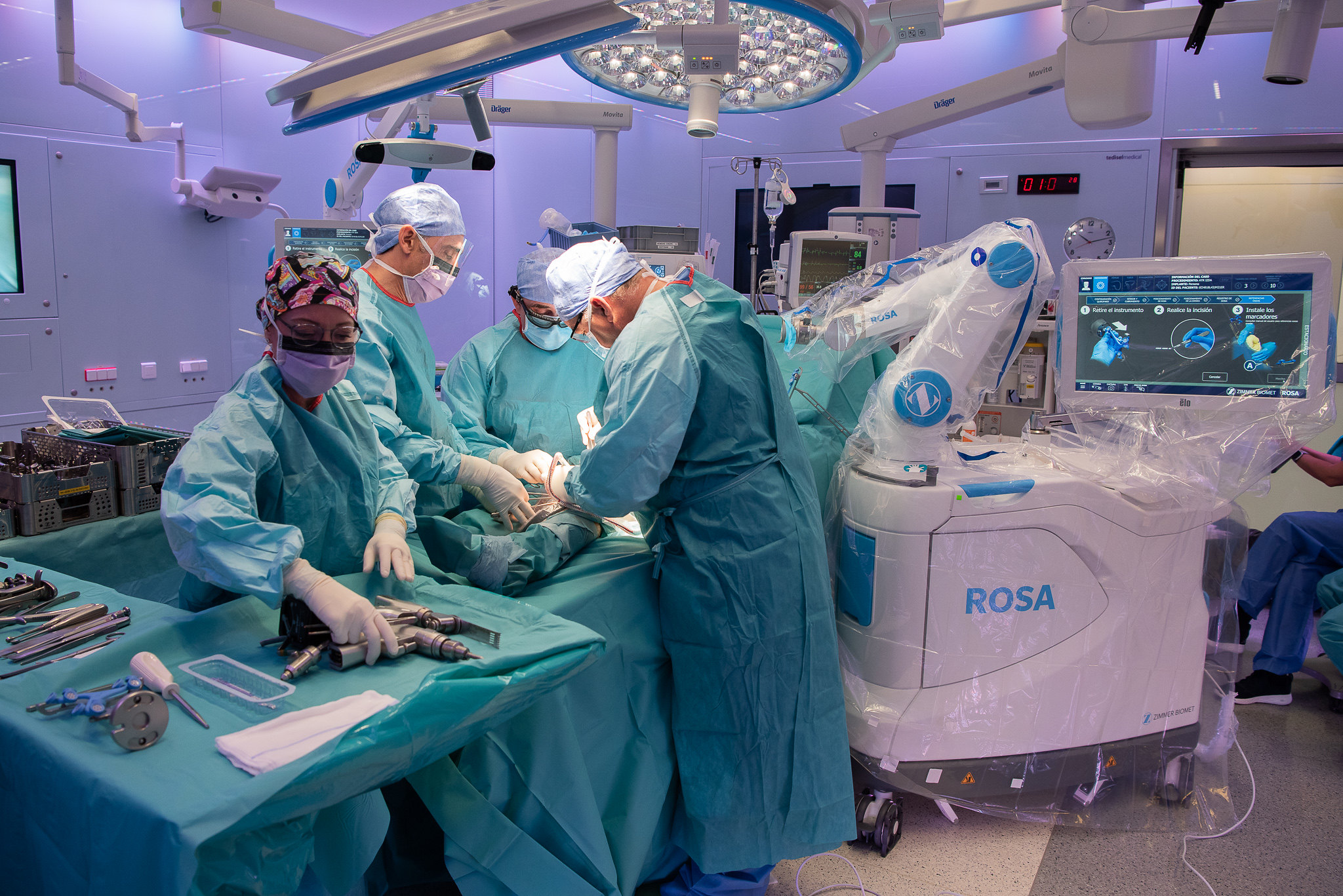
Choosing the right facility for joint replacement surgery in Europe can be a daunting process, especially for healthcare professionals tasked with referring patients to suitable clinics. With advancements in medical technology and the increasing specialization of orthopedic care, understanding how to choose the best orthopedic clinics for joint replacement in Europe becomes essential. This guide aims to break down the complexities involved in choosing orthopedic clinics for joint replacement, providing insights into critical factors such as clinic accreditation, specialist qualifications, and patient success rates. By exploring joint replacement surgery options in Europe and highlighting the best orthopedic clinics for joint replacement, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions that significantly impact patient outcomes. Additionally, this post will offer valuable tips for choosing orthopedic clinics for joint surgery, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the available options throughout the continent.
Understanding Joint Replacement Surgery
Joint replacement surgery is a significant medical procedure aimed at alleviating pain, restoring mobility, and improving the overall quality of life for patients suffering from debilitating joint conditions. It typically involves the removal of damaged joint surfaces and replacement with artificial components, made from durable materials such as metal, plastic, or ceramics. Given its complexity and the various factors influencing the outcomes, a comprehensive understanding of this surgery is essential for healthcare professionals directing patients towards appropriate care.
Key Types of Joint Replacement Surgeries
The most commonly performed joint replacement surgery options in Europe include:
- Knee Replacement: This procedure involves removing the damaged cartilage and bone in the knee joint and replacing them with metal and plastic components. It is especially beneficial for patients with osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or severe knee injuries.
- Hip Replacement: Hip replacement surgery entails substituting the hip joint with artificial implants, which helps relieve severe pain and improve mobility. This procedure is commonly recommended for patients with hip fractures or conditions such as osteoarthritis.
- Shoulder Replacement: In cases of severe arthritis or trauma, shoulder replacement surgery can help restore function and decrease pain. It typically involves replacing the damaged joint surfaces with artificial components.
- Ankle Replacement: Although less common than other joint replacement surgeries, ankle replacement is an option for patients suffering from arthritis or significant ankle joint degradation.
Indications for Joint Replacement Surgery
Healthcare professionals should be aware of several factors that may necessitate joint replacement surgery:
- Chronic Pain: Patients experiencing persistent pain in joints that does not respond to conservative treatments may be candidates for surgery.
- Functional Impairment: Difficulty in performing everyday activities due to joint issues often leads patients to consider surgical options.
- Joint Deformity: Significant deformities can limit mobility, making joint replacement a suitable approach to restoration.
Benefits of Joint Replacement Surgery
The advantages patients can expect from joint replacement are substantial and can be summarized as follows:
- Pain Relief: Most patients report a significant reduction in joint pain following surgery.
- Improved Joint Functionality: Enhanced movement and ability to engage in normal activities are common post-operative results.
- Increased Quality of Life: The overall enhancement in physical ability and freedom from pain contributes to better mental well-being.
Risks and Considerations
While the benefits are considerable, healthcare professionals must also communicate the potential risks associated with joint replacement:
- Infection: Although rare, surgical site infections can occur and lead to complications.
- Blood Clots: Patients may face an increased risk of clot formation post-surgery, which requires monitoring.
- Artificial Joint Failure: In some cases, the artificial components may wear out or fail, necessitating additional surgeries.
Conclusion
Understanding joint replacement surgery is crucial for healthcare professionals in guiding patients toward the best options. Leveraging knowledge of the types of surgeries available, indications for surgery, expected benefits, and associated risks enables clinicians to provide informed recommendations. As healthcare continues to evolve, knowledge of advancements in techniques and materials used in joint replacements remains a vital component of comprehensive patient care, ultimately improving the chances of successful outcomes in best orthopedic clinics for joint replacement in Europe.

Factors to Consider When Choosing Orthopedic Clinics
Selecting the right orthopedic clinic for joint replacement surgery is crucial, as it significantly impacts patient outcomes and satisfaction. Choosing orthopedic clinics for joint replacement involves evaluating various factors to ensure both quality and safety. Here are some key considerations that healthcare professionals should take into account:
1. Reputation and Specialization of the Clinic
- Investigate the clinic’s reputation in the medical community. Look for endorsements from other healthcare professionals and patient testimonials.
- Select clinics that specialize in joint replacement surgery specifically, as these facilities often have more advanced technology and specialized staff for handling complex cases.
2. Accreditation and Certification
- Verify whether the clinic is accredited by reputable organizations. Accreditation signifies that the clinic meets specific health and safety standards.
- Consider clinics that have received certifications from international bodies, which ensures compliance with global quality benchmarks.
3. Experience of the Orthopedic Specialists
- The experience and qualifications of the orthopedic surgeons are paramount. Research their educational background, training, and specialized areas.
- Ensure that the surgeons have a significant number of successful joint replacement surgery options in Europe under their belt, specifically those that align with the needs of the patient.
4. Technology and Facilities
- Evaluate the type of technology and equipment available at the clinic. State-of-the-art facilities often contribute to improved surgical outcomes and shorter recovery times.
- Check if the clinic uses minimally invasive surgical techniques, which can significantly reduce recovery time and minimize the extent of physical trauma.
5. Success Rates and Outcomes
- Research the clinic’s published success rates for joint replacement surgeries. High success rates are indicative of effective practices and satisfied patients.
- Consider the types of records the clinic maintains regarding patient outcomes, such as postoperative complications or the need for revision surgeries.
6. Patient Care and Support Services
- Assess the overall patient care provided by the clinic. Good clinics prioritize patient comfort and communication, offering preoperative education and postoperative follow-up.
- Look for facilities that provide access to comprehensive rehabilitation programs, which can enhance recovery after joint replacement surgery in Europe.
7. Cost and Insurance Options
- Understand the costs associated with surgery in various clinics. While it is essential to consider affordability, do not compromise on quality for price.
- Clarify whether the clinic accepts the patient’s insurance, and outline any additional out-of-pocket expenses that may arise.
Quick Reference Table
| Factor | Key Consideration | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Reputation | Endorsements and testimonials | Indicates credibility |
| Accreditation | Valid certifications from recognized bodies | Ensures quality and safety standards |
| Specialist Experience | Track record of orthopedic surgeons | Affects surgical outcomes |
| Technology and Facilities | Use of advanced medical equipment | Impacts recovery efficiency |
| Success Rates | Documented statistics for previous surgeries | Reflects effectiveness of the clinic |
| Patient Care and Support Services | Quality of pre-op and post-op support | Enhances overall patient experience |
| Cost and Insurance Considerations | Coverage options and limits | Essential for financial planning |
By thoroughly evaluating these factors, healthcare professionals can adeptly guide patients in choosing the best orthopedic clinics for joint replacement in Europe. The ultimate goal is to ensure that patients receive the highest quality care in a supportive and efficient environment.
Evaluating the Best Orthopedic Clinics in Europe
When exploring How to Choose the Best Orthopedic Clinics for Joint Replacement in Europe, healthcare professionals must prioritize a comprehensive evaluation of various clinics. Given the diversity in healthcare quality, facilities, and patient outcomes across Europe, the process of making an informed choice can be overwhelming. Thus, a structured approach to evaluating the Best Orthopedic Clinics in Europe is essential for guiding patients towards effective joint replacement solutions.
Key Evaluation Criteria
- Accreditations and Certifications:
- It is crucial to ensure that clinics hold valid accreditations from recognized authorities. These certifications not only indicate quality care but also adherence to international standards of practice.
- Technology and Facilities:
- Investigating the type of technology used in joint replacement surgeries is essential. Facilities equipped with the latest orthopedic surgical technology often lead to better patient outcomes. Additionally, the presence of advanced rehabilitation services post-surgery can significantly affect the recovery process.
- Physician Expertise:
- The experience and specialization of orthopedic surgeons play a vital role. Evaluate the surgeons’ educational backgrounds, years of experience, and the volume of joint replacement surgeries performed. According to statistics, higher volumes typically correlate with better outcomes.
- Success Rates:
- Clinics should be able to provide success rates for specific procedures. A high percentage of successful surgeries indicates proficiency and patient satisfaction. Request data that reflect the clinic’s track record for specific joint replacements.
- Patient Testimonials and Reviews:
- A thorough investigation into patient feedback helps gauge the clinic’s reputation. Consider checking platforms like HealthGrades or real patient testimonials on the clinic’s website. Positive reviews regarding the surgical experience, staff professionalism, and post-operative care are key indicators of quality.
Comparison Table of Top-Rated Orthopedic Clinics in Europe
| Clinic Name | Location | Accreditation | Success Rate (%) | Patient Ratings (out of 5) | Technology Used |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Royal Orthopaedic Hospital | Birmingham, UK | JCI, ISO 9001 | 94% | 4.8 | Robotics, 3D printing |
| Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin | Berlin, Germany | DIN EN ISO 9001 | 90% | 4.6 | Minimally invasive surgery |
| Hospital for Special Surgery | New York, USA | JCAHO, AAHRPP | 92% | 4.7 | Advanced imaging techniques |
| Clinica Santa Maria | Lisbon, Portugal | Joint Commission | 91% | 4.5 | Hybrid operating rooms |
Insights from Healthcare Professionals
“In selecting the best orthopedic clinics for joint replacement, it is imperative to utilize a mixture of quantitative and qualitative data. Understanding a clinic’s clinical outcomes alongside patient experiences presents a clearer picture of the facility’s overall capability.”
Such insights underscore the necessity of a holistic evaluation that incorporates data-driven analysis with an understanding of patient-centric care.
Conclusion
In navigating the landscape of joint replacement surgery options in Europe, healthcare professionals equipped with the right evaluation tools can significantly impact their patients’ surgical outcomes. By emphasizing modern technology, qualified specialists, and strong accreditation, professionals stand to guide patients toward the top-rated orthopedic hospitals for joint replacement in Europe, ensuring successful procedures and overall satisfaction.
Top-rated Orthopedic Hospitals for Joint Replacement
Identifying the best orthopedic clinics for joint replacement in Europe is a crucial task for healthcare professionals tasked with recommending suitable treatment options for their patients. Europe boasts an array of top-rated orthopedic hospitals, which offer advanced joint replacement procedures along with cutting-edge technology and exceptional patient care. This section will detail some of the leading institutions renowned for their expertise and success rates in joint replacement surgery, making it easier for healthcare providers to guide their patients effectively.
Notable Orthopedic Hospitals in Europe
The following table outlines key attributes of several top-rated orthopedic hospitals across Europe, helping professionals understand the strengths of each facility:
| Hospital Name | Location | Specialization Focus | Accreditation | Patient Satisfaction Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cleveland Clinic | London, UK | Joint Replacement & Rehabilitation | JCI Accreditation | 92% |
| Charité – Universitätsmedizin | Berlin, Germany | Orthopedic Surgery & Sports Medicine | DIN EN ISO 9001 Certified | 90% |
| Hospital for Special Surgery | Paris, France | Minimally Invasive Joint Surgery | COFACE Certification | 95% |
| Hospital Universitario de La Princesa | Madrid, Spain | Innovative Joint Techniques | Joint Commission International (JCI) accredited | 88% |
| San Raffaele Hospital | Milan, Italy | Robotic Joint Replacement | Healthcare Quality Accreditation (ISQua) | 91% |
Key Features of Top-rated Orthopedic Hospitals
- Experienced Healthcare Teams: The forefront of orthopedic care lies in the expertise of the surgical teams. These hospitals are home to world-class orthopedic surgeons, many of whom are pioneers in innovative surgical techniques. Their experience plays a crucial role in effective joint replacement surgery outcomes.
- Specialized Equipment: Top-rated clinics invest heavily in specialized tools and technology, such as robotic-assisted surgical systems. This advancement leads to more precise surgeries, enhanced recovery times, and better overall patient satisfaction.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: Many of the best orthopedic clinics in Europe adopt a multidisciplinary approach to patient care, involving physiotherapists, occupational therapists, and nutritionists. This ensures that patients receive comprehensive support throughout their recovery process.
- Research and Innovation: These hospitals often collaborate with academic institutions, contributing to research that pushes the boundaries of orthopedic surgery. Patients benefit from being treated with the most advanced techniques and protocols.
- International Patient Services: Many leading institutions are well-equipped to cater to international patients. This includes translation services, pre-travel consultations, and assistance with logistics, which can alleviate much of the stress associated with traveling for medical care.
Making Informed Referrals
When recommending hospitals, healthcare professionals must consider not only the reputation of these institutions but also their accessibility, surgical outcomes, and the experiences of previous patients. Visiting the websites of these top-rated orthopedic hospitals for joint replacement can provide invaluable insights into their services, facilities, and innovative approaches.
With an array of options available, evaluating aspects such as technological capacity, surgical success rates, and patient comfort should remain at the forefront of any referral. By leveraging this information, healthcare professionals can help patients make informed choices regarding joint replacement surgery options in Europe, ensuring they receive the highest standard of care during their treatment journey.
Assessing the Qualifications of Orthopedic Specialists
When it comes to ensuring a successful joint replacement surgery in Europe, the qualifications and expertise of orthopedic specialists play a pivotal role in patient outcomes. Selecting the right orthopedic surgeon is vital, as their skills and knowledge significantly influence the surgery’s effectiveness and the patient’s post-operative recovery. Therefore, healthcare professionals must thoroughly assess these qualifications before making referrals. This section will explore key considerations in evaluating orthopedic specialists.
Key Qualifications to Assess:
- Education and Training:
- Look for orthopedic surgeons with completed medical degrees from recognized institutions.
- Ensure they have undergone specialized training in orthopedic surgery and joint replacement surgery specifically.
- Consider post-graduate fellowships that enhance their skills, particularly those focusing on joint surgery.
- Board Certification:
- Verify that the specialist is board-certified in orthopedic surgery, recognized by relevant medical boards or authorities.
- Board certification indicates that the surgeon has met national standards in education, skills, and knowledge essential for orthopedic practices.
- Experience:
- Analyze the number of joint replacement surgeries the specialist has performed, focusing on their specific expertise in the type of joint replacement being considered.
- Generally, a surgeon with a higher volume of surgeries in the relevant area may lead to better outcomes.
- Specialization:
- Identify if the surgeon specializes in specific joint replacements (e.g., hip, knee, shoulder) which may indicate a more refined expertise in that area.
- This can be particularly important since different joint surgeries have distinct techniques and recovery protocols.
- Research and Publications:
- Review any research involvement or publications by the orthopedic specialist. Contributions to academic journals can signify a commitment to staying updated with the latest advancements and techniques in orthopedic surgery.
The Role of Hospital Affiliations:
The hospital where the orthopedic specialist practices can significantly impact the quality of care. Here are some points to consider regarding affiliations:
- Affiliated Institutions: Check if the orthopedic specialist is affiliated with top-rated orthopedic hospitals for joint replacement in Europe. Renowned institutions often have rigorous standards for their staff.
- Access to Technology: Ensure the affiliated hospital has advanced technology and facilities that support complex orthopedic procedures. Cutting-edge technology can facilitate better surgical outcomes and quicker patient recovery.
Certification and Memberships:
Healthcare professionals should also take into account any relevant certifications and memberships. This can include:
- Professional Associations: Membership in professional organizations like the European Orthopedic Association indicates ongoing commitment to professional development and adherence to best practices.
- Research Credentials: Participation in symposiums or workshops can showcase the surgeon’s dedication to advancing their knowledge and skills in joint replacement surgery options in Europe.
By evaluating these qualifications thoroughly and systematically, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions when referring patients to orthopedic specialists. Choosing orthopedic specialists for joint replacement is a crucial step that can lead to enhanced surgical success rates and better patient experiences.
Summary Table of Key Qualifications
| Qualification Type | Importance |
|---|---|
| Education and Training | Foundation of surgical knowledge and skills. |
| Board Certification | Ensures adherence to national standards. |
| Experience | Greater experience often correlates with better outcomes. |
| Specialization | Indicates refined expertise in specific joint replacements. |
| Research and Publications | Reflects commitment to the latest advancements. |
| Hospital Affiliations | Direct correlation to the quality of care. |
| Certifications and Memberships | Ensures adherence to best practices and ongoing training. |
By providing a meticulous assessment of these crucial elements, healthcare professionals can ensure their patients receive the highest standard of care in the field of orthopedic surgery as they explore the best orthopedic clinics in Europe for joint replacement surgery options.
Comparing Joint Replacement Surgery Options in Europe
When it comes to joint replacement surgery options in Europe, healthcare professionals must have a comprehensive understanding of the various methodologies available. Europe is renowned for its advanced healthcare systems, making it a prime location for patients seeking orthopedic procedures. Several surgical techniques and implant options can impact the overall patient experience and recovery.
Types of Joint Replacement Surgeries
Joint replacement surgeries may vary significantly based on the joint involved, the surgical technique employed, and the type of implants used. Here are some commonly recognized joint replacement options:
- Total Joint Replacement (TJR): This involves replacing the entire joint with prosthetic components. It is commonly performed on hips and knees.
- Partial Joint Replacement: Only a part of the joint surface is replaced. This option is less invasive and often results in quicker recovery times.
- Revision Joint Replacement: This procedure is undertaken to replace or fix an already-implanted joint prosthesis that may have failed or deteriorated over time.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery (MIS): This technique utilizes smaller incisions, promoting quicker recovery and significantly less postoperative pain.
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery: An emerging technique that employs robotic systems to enhance precision in placement and alignment of implants during surgery.
Comparing Procedural Effectiveness
To effectively assess joint replacement surgery options in Europe, several criteria should be analyzed:
- Success Rates: Compare the success rates of various surgical techniques for the specific joint being treated. This data is typically accessible through national or regional health registries.
- Recovery Times: Evaluate the average recovery times associated with each procedure. Minimally invasive techniques often lead to shorter hospital stays and faster rehabilitation.
- Patient Satisfaction: Look into patient-reported outcomes, including satisfaction rates with pain relief and functional improvements post-surgery.
- Complication Rates: A vital aspect when comparing these options is understanding the potential complications associated with each surgical method, which can vary significantly.
Cost Analysis
In terms of costs, joint replacement surgery options in Europe can differ, making it essential for healthcare professionals to have insights into the financial implications. Here’s a comparison of potential costs:
| Procedure Type | Average Cost in Europe | Length of Stay | Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Joint Replacement | €10,000 – €20,000 | 4-7 days | 6-12 weeks |
| Partial Joint Replacement | €8,000 – €15,000 | 3-5 days | 4-8 weeks |
| Revision Joint Replacement | €15,000 – €25,000 | 5-10 days | 8-16 weeks |
| Minimally Invasive Surgery | €12,000 – €22,000 | 2-4 days | 3-6 weeks |
Selecting the Right Procedure
When considering the best orthopedic clinics for joint replacement in Europe, healthcare professionals should inquire about the following:
- Protocols and guidelines: Are evidence-based protocols in place to guide the choice of procedure?
- Preoperative assessments: Is a comprehensive preoperative assessment conducted to determine the most suitable option for the patient?
- Follow-up care: Are there structured follow-up procedures to monitor the patient’s recovery and address any complications early on?
Platforms like the European Society of Sports Traumatology, Knee Surgery, and Arthroscopy (ESSKA) often provide valuable information regarding ongoing studies and procedure effectiveness, offering excellent resources for healthcare professionals to stay informed about joint replacement surgery options in Europe.
In summary, comparing joint replacement surgery options in Europe requires diligent evaluation of several critical factors, including surgical techniques, success and complication rates, and associated costs. By thoroughly examining these elements, healthcare professionals can ensure they provide informed recommendations to their patients, maximizing the chance for successful outcomes.
The Importance of Clinic Accreditation and Certification
When seeking the best orthopedic clinics for joint replacement in Europe, understanding the significance of clinic accreditation and certification is pivotal. Accreditation serves as a formal recognition that a healthcare facility meets specific standards of quality and safety in patient care. As a healthcare professional, recognizing these standards is crucial not only for ensuring the potential success of the procedures but also for safeguarding patient welfare.
Key Benefits of Accreditation
- Quality Assurance: Accreditation ensures that the clinic adheres to rigorous, international standards in surgical protocols and patient management. Accredited facilities routinely undergo evaluations to verify compliance with the latest healthcare practices.
- Patient Safety: Safety is paramount in any surgical context. Accredited clinics are required to implement safety measures that minimize the risk of infection, surgical errors, and post-operative complications. This translates into a higher level of care for patients undergoing joint replacement surgery in Europe.
- Transparency: Accreditation bodies often have publicly accessible records. This openness fosters trust, allowing healthcare professionals to assess a clinic’s reputation based on independently reviewed quality indicators.
- Access to Advanced Technology: Many accredited facilities invest heavily in the latest technology and treatment protocols. This access typically leads to better patient outcomes, making it easier for healthcare providers to recommend specific clinics.
- Continuous Improvement: Accredited clinics are often engaged in quality improvement initiatives that aim to enhance service offerings continuously. This proactive approach aligns well with the evolving nature of orthopedic care, ensuring that patients receive current and effective treatments.
How to Verify Accreditation
- Check Accreditation Bodies: Look for affiliations with reputable organizations such as the Joint Commission International (JCI) or national healthcare accreditation bodies. These entities set benchmarks in quality and safety for healthcare providers.
- Review Certification Levels: Many clinics possess multiple certifications that highlight their specialization in joint replacement procedures. Understanding these can help in evaluating the facility’s focus on orthopedic care.
- Research Awards and Recognitions: Clinics often participate in competitions or evaluations, earning awards that reflect their commitment to excellence in patient care.
Accreditation as a Benchmark for Specialists
Additionally, the certification status of the orthopedic specialists associated with a clinic can provide further layers of reassurance. Specialists with board certifications from recognized professional organizations have typically met extensive training and experience requirements. Here’s a quick comparison of certification methods:
| Certification Type | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Board Certification | Indicates specialists have passed comprehensive exams and maintained training. | Ensures higher competency in specific areas. |
| Fellowship Training | Involves advanced training in orthopedic surgery post-residency. | Signifies expertise in complex joint procedures. |
| Continuous Medical Education | Requires ongoing education and training to maintain credentials. | Confirms up-to-date knowledge of best practices. |
Recognizing the importance of clinic accreditation and certification enables healthcare professionals to offer informed referrals to patients seeking joint replacement surgery options in Europe. It not only equips them with thorough knowledge about the quality of care offered but also highlights a strong commitment to patient safety and successful outcomes. By choosing best orthopedic clinics for joint replacement, healthcare professionals can play a crucial role in enhancing overall patient experiences and surgical success rates.
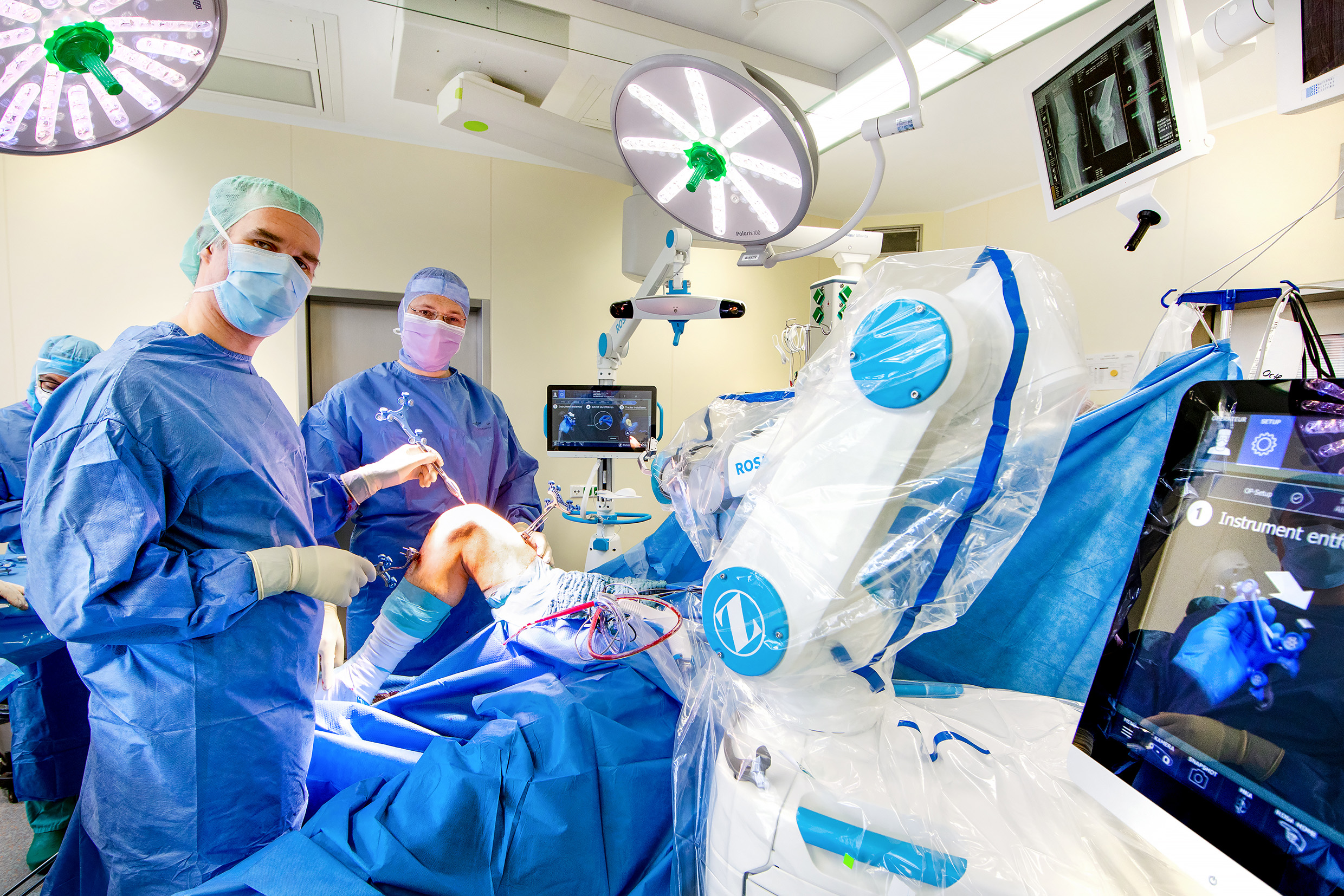
Patient Reviews and Success Rates of Orthopedic Clinics
When evaluating the best orthopedic clinics for joint replacement in Europe, one vital factor is the collection and analysis of patient reviews and success rates. In an era of rapid information sharing, healthcare professionals and patients alike should leverage these insights to gauge which facilities truly deliver on their promises of quality care and successful outcomes. Here, an in-depth examination of patient feedback and clinical success metrics will be discussed, highlighting its critical role in choosing orthopedic clinics for joint replacement.
Importance of Patient Reviews
Patient reviews serve as a direct reflection of the experiences that individuals have undergone during their treatment. They often encompass various elements, such as:
- Quality of Care: Patients frequently share how attentive and compassionate the medical staff was throughout the process.
- Surgical Outcomes: Many reviews detail recovery experiences and overall satisfaction post-surgery.
- Clinic Environment: The cleanliness and organization of the facility can significantly affect patient comfort.
To effectively interpret these reviews, healthcare professionals are advised to consider both quantitative ratings and detailed narratives. For example:
- Star Ratings: Clinics might be rated on a scale of 1 to 5. A higher rating usually reflects a better experience.
- Review Platforms: Websites such as Healthgrades or RealSelf tend to offer verified patient feedback, adding credibility to the reviews.
Assessing Success Rates
In tandem with patient reviews, clinics often publish their joint replacement surgery options in Europe success rates, which can provide quantitative backing to their claims. Understanding the statistical success of orthopedic procedures can significantly inform decision-making for patients and healthcare providers. Key aspects to consider include:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Surgical Success Rate | The percentage of surgeries with positive outcomes (e.g., reduced pain, improved mobility). |
| Complication Rate | The percentage of surgeries that resulted in complications, which can indicate the quality of care. |
| Reoperation Rate | The percentage of patients who required additional surgeries within a specified timeframe, revealing potential issues with the original procedure. |
| Patient Satisfaction Score | Often collected through surveys post-discharge, this metric reflects patients’ overall satisfaction with their care experience. |
Sources of Success Rate Data
While patient reviews can be highly subjective, institutional success rates are often based on concrete data collected during preferences studies, audits, or accreditation assessments. Credible sources where healthcare professionals can find statistics include:
- National Joint Registries: Many countries maintain databases that track the outcomes of joint replacement surgeries—an excellent resource for obtaining benchmarks.
- Hospital Websites: The best orthopedic clinics in Europe often feature transparency by posting their success rates and outcomes publicly.
- Peer-reviewed Journals: Published studies can contribute valuable insights into specific techniques or innovations that drive better outcomes.
Making Informed Choices
When healthcare professionals recommend orthopedic clinics to their patients, emphasizing the significance of both patient reviews and success rates can empower informed decision-making. By considering factors such as:
- Trends in Reviews: Regularly evaluate if certain issues are recurring, which might indicate underlying problems.
- Comparative Analysis: Assess success rates against national averages or equivalent facilities to ascertain relative performance.
Through due diligence in examining these dimensions, healthcare experts can support their patients in choosing orthopedic specialists for joint replacement who are not only skilled but also demonstrate a proven track record of success in joint replacement surgery in Europe. This diligent approach ensures patients receive the highest quality of care tailored to their individual needs.
Cost Considerations for Joint Replacement Surgery in Europe
Joint Replacement Surgery can be a vital procedure for patients suffering from debilitating conditions, but financial considerations cannot be overlooked. The cost of joint replacement surgery options in Europe varies considerably, influenced by factors such as the clinic’s location, the type of procedure, and the quality of post-operative care. For healthcare professionals needing to refer patients, understanding these cost implications is crucial.
Factors Influencing the Cost of Joint Replacement Surgery
The following factors play a significant role in determining the final cost of joint replacement surgery options in Europe:
- Geographical Location: Different countries and even cities within Europe offer varied pricing for surgeries due to economic conditions and healthcare costs. For instance, countries such as Germany and Switzerland typically have higher costs compared to Poland or Hungary.
- Type of Joint Replacement: Procedures like total knee replacement may have different price points compared to partial replacements. The complexity of the surgery directly impacts the pricing.
- Hospital Accreditation: Top-rated orthopedic hospitals for joint replacement in Europe may charge more due to their advanced facilities and high standards of care. Accredited clinics often provide better patient outcomes, which can justify the higher expenses.
- Length of Hospital Stay: Costs can escalate based on the duration a patient stays in the clinic post-surgery. Hospitals may recommend a longer recovery period, which can add to the overall charges.
- Rehabilitation Services: Post-operative rehabilitation is a critical component for the overall success of joint replacement. Many clinics offer bundled services, and understanding these packages can aid in cost estimation.
Average Costs of Joint Replacement Surgery
Here’s a simplified comparison table showcasing average costs for common types of joint replacement surgery in Europe:
| Type of Surgery | Average Cost (EUR) | Country |
|---|---|---|
| Total Knee Replacement | 12,000 – 15,000 | Germany |
| Total Hip Replacement | 10,000 – 14,000 | Austria |
| Partial Knee Replacement | 8,000 – 12,000 | Hungary |
| Shoulder Replacement | 9,000 – 13,000 | Spain |
| Ankle Replacement | 10,000 – 12,500 | France |
Financial Aid and Insurance Coverage
- Insurance Options: Patients are encouraged to explore their health insurance plans to understand coverage limits and out-of-pocket expenses. Some clinics in Europe may have arrangements with international insurance companies, facilitating a smoother financial process.
- Payment Plans: Many best orthopedic clinics for joint replacement offer flexible payment options and financing plans, making it more manageable for patients undergoing surgery.
- Cost Transparency: Clinics are increasingly providing cost breakdowns upfront, ensuring patients and healthcare providers are fully aware of potential expenses.
“In Europe, the cost of joint replacement surgery can be significantly lower compared to the United States, without compromising on quality. Thus, it is vital for healthcare professionals to inform patients about their options and the associated costs when considering surgery abroad.”
Ultimately, when considering joint replacement surgery Europe, cost should be weighed alongside quality and outcomes. As healthcare professionals refer patients, their understanding of the financial landscape, including potential hidden costs, may greatly influence patient decisions regarding surgery. This knowledge empowers both clinicians and patients to make informed choices, ensuring the best possible outcomes post-surgery.
Tips for Healthcare Professionals in Referring Patients
Referring patients to specialized orthopedic clinics for joint replacement surgery can be a vital aspect of a healthcare professional’s responsibilities. Given the myriad options available, healthcare professionals must be well-informed when recommending best orthopedic clinics for joint replacement in Europe. Here are several key tips to streamline the referral process and assist patients in obtaining optimal surgical care.
1. Understand Patient Needs and Preferences
It is crucial for healthcare professionals to communicate effectively with patients to understand their needs. Consider the following:
- Patient’s Medical History: Thoroughly review the patient’s medical history, previous surgeries, and any comorbidities that may affect the surgical outcome.
- Location Preferences: Some patients may prefer clinics in specific countries or regions within Europe. Understanding these preferences can simplify the referral process.
- Cultural Considerations: Acknowledge cultural beliefs and practices that may influence a patient’s choice in pursuing joint replacement surgery in Europe.
2. Research Reconciling Safety and Quality
As a healthcare professional, you must ensure that you only refer patients to top-rated orthopedic hospitals for joint replacement in Europe. Investigate:
- Accreditation Status: Verify whether the clinic holds necessary accreditations and certifications, indicating a commitment to quality care.
- Reputation: Utilize peer-reviewed articles and industry reports to assess each clinic’s reputation. Seek feedback from other healthcare professionals.
- Technological Advancements: Inquire about the advanced technologies utilized in the clinics, which can provide better patient outcomes.
3. Networking and Collaboration
Building a network of trusted orthopedic specialists is vital:
- Establish Professional Relationships: Maintain relationships with prominent orthopedic clinics and surgeons to have firsthand knowledge of their services and success rates.
- Professional Conferences: Attend relevant topic-specific conferences to learn about new techniques and connect with leading specialists within the European medical landscape.
4. Utilize Patient Reviews and Outcomes Data
Patient feedback is invaluable in assessing orthopedic clinics:
- Analyze Testimonials: Encourage patients to look up patient reviews online, which can provide insights into personal experiences regarding specific clinics.
- Review Success Rates: Websites often provide metrics on success rates for joint replacement surgeries. Use this data to compare and contrast clinics objectively.
5. Educate Patients on Joint Replacement Surgery Options
Educating patients about their choices plays a pivotal role:
- Discuss Different Surgical Techniques: Familiarize yourself with various joint replacement surgery options in Europe, such as minimally invasive techniques, as each may have different recovery times and outcomes.
- Specify Post-Operative Care: Outline the post-operative care and rehabilitation services provided by clinics, ensuring a smooth recovery for the patient.
6. Address Cost Considerations
Economics can be a knowledge barrier in the referral process:
- Inform About Insurance Coverage: Discuss patients’ insurance plans and what costs they may be responsible for, as this can influence their selection of clinics.
- Transparency in Pricing: Help patients seek clinics that provide transparent pricing structures and detailed breakdowns of the total costs involved in joint replacement surgery Europe.
7. Follow-Up and Monitor Outcomes
Lastly, follow-up is essential:
- Track Patient Recovery: Monitor the patient’s progress post-surgery when referred to a clinic. Keeping in touch with both patients and clinic staff ensures a continuum of care.
- Feedback Loop: Encourage feedback from patients relating to their experiences with the clinic, providing valuable information for future referrals.
By following these tips, healthcare professionals can effectively guide patients in choosing the best orthopedic clinics for joint replacement in Europe, ensuring they receive adequate care tailored to their needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What criteria should one consider when choosing an orthopedic clinic for joint replacement in Europe?
When selecting an orthopedic clinic for joint replacement in Europe, several key criteria should be considered. These include the clinic’s accreditation and certifications, the experience and qualifications of the orthopedic surgeons, the range of technology and techniques employed, and the clinic’s overall success rates in joint replacement procedures. Additionally, it’s important to assess the quality of patient care, available rehabilitation services, and reviews or testimonials from previous patients to ensure a comprehensive evaluation of the clinic’s reputation.
Are there specific countries in Europe that are known for their orthopedic clinics?
Yes, certain countries in Europe are renowned for their exceptional orthopedic clinics and healthcare systems. Nations such as Germany, Switzerland, and Austria are often cited for their advanced medical practices and state-of-the-art facilities. These countries are known for their highly skilled orthopedic surgeons and favorable patient outcomes in joint replacement surgeries. Furthermore, other countries like the UK and France have established clinics with strong track records, making them viable options for those seeking orthopedic care.
How can patients ensure they receive the best care during and after their joint replacement surgery?
Patients can take several proactive steps to ensure they receive the best care during and after their joint replacement surgery. Firstly, they should thoroughly research and consult with multiple clinics to understand their options. Engaging in pre-surgery consultations allows patients to discuss their concerns and expectations with the surgical team. Post-surgery, adhering to rehabilitation protocols, attending follow-up appointments, and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers is crucial for optimal recovery. Patients should also understand their role in their recovery by following prescribed exercises and lifestyle modifications.
What is the average cost of joint replacement surgery in Europe?
The average cost of joint replacement surgery in Europe can vary significantly depending on the country, clinic, and the specifics of the procedure. Generally, prices can range from €10,000 to €30,000. Countries in Western Europe such as Germany and Switzerland tend to have higher costs, while Eastern European countries can offer more competitive pricing without compromising quality. It’s vital for patients to inquire about all associated costs, including pre-operative assessments, anesthesia, post-operative care, and rehabilitation services, to obtain a complete picture of the financial investment required.